Modal phrases or semi modals are used to express the same things as modals but are a combination of auxiliary verbs and the preposition to. They are also known as modal auxiliaries or modal auxiliary verbs. They are different from normal verbs like eat, drink, visit, laugh, jump, dance, follow, etc. They give additional information about the function of the main verb that comes after it.
These are verbs that express different kinds of things. When you use them, they express certainty, ability, willingness, necessity, permission, obligation, and possibility. Since they behave differently from regular verbs, they are a little confusing. Modals are those helping verbs that express the mode of action denoted by the main verb. These modals are used to express ability, power, permission, request, possibilities, willingness, etc. They have a special place in the English language as they perform certain structural function in sentence formation.
In this unit you will see how we can form sentences to communicative various language functions using them. You will realize that composing sentences using tenses is not enough and all things cannot be expressed using tenses, all language functions cannot be done using only tenses. Modal Auxiliaries help us in doing functions like warning some one, making suggestions, giving advice, threatening others, talking about memories, etc. Good understanding of these modal auxiliaries is necessary to form various sentences. As usual like tenses we shall study them as 'structure words' for sentence formation for various language functions.
Modal verbs are so common that most English speakers don't even know what the grammatical name for them is. Note that modal auxiliary verbs are a type of auxiliary verb. Auxiliary verbs encompass tenses, aspects, modality , voice, emphasis and so on.
There are many other category of verbs in English like phrasal verbs. In this ESL skills course you can learn natural English phrases. Learn even more about English grammar in this introduction to grammar course. Modal auxiliary verbs are used to show a necessity, capability, willingness, or possibility.
Unlike most verbs, there is only one form of these verbs. Typically, verb forms change to indicate whether the sentence's structure is singular or plural. Most verbs also indicate whether something happened in the past, present, or future.
This is not the case with most modal auxiliary verbs, which makes them simpler to understand and use correctly. Permission supposition with doubt if not prohibition. The modal verbs of english are a small class of auxiliary verbs used to express possibility obligation advice permission ability. Modals are auxiliary verbs i.e., helping verbs which express the modality of a statement or a main verb. Modality could be anything starting from the request, likelihood, permission, ability, capacity, suggestions, orders, obligations to advice.
So, basically, the Modal verbs are used along with the main verb in order to give additional information regarding its nature. For instance, consider the statement given below. In English, the modal verbs are used to express ability, possibility, permission or obligation.
What Are Modal Verbs Explain With Each one of the modal verbs can be used to express one or more of these modalities. They can also be used to form the future tense in English and to make conditional sentences. Modal verbs are followed by a base verb the plain dictionary definition of a verb like jump help sing play or read. Learn the list of modal verbs in english with grammar rules and example sentences. The modal auxiliary verbs are never used as a main verb. In addition, they do not have the five forms that main verbs have.
While other auxiliary verbs can be used as a main verb and have the five forms, these modal auxiliary verbs do not. Remember that modal verbs are auxiliary verbs, or helping verbs, that are most commonly used to talk about possibility or necessity. You can also use modal verbs to ask for and give permission, describe ability, and give advice.
In English, modal verbsare a small class of auxiliary verbs used to express ability, permission, obligation, prohibition, probability, possibility, advice. In grammar, a modal or a modal auxiliary is a word such as 'can' or 'would' which is used with a main verb to express ideas such as possibility, intention, or necessity. It contains a verb phrase that is followed by a subject.
In these three statements, "dare", "can" and "may" are the modals. If you look closer at them you will understand what we mean by the statement that modals express modality. In the first statement, the Modal "dare" shows that it's an order. In the second statement, "can" signifies the ability of the subject "I" and in the third one, the word "may" highlights some possibility. So, the Modals used in these sentences give us some additional information about the main verb, noun or subject of the statement.
Have to is often grouped with modal auxiliary verbs for convenience, but in fact it is not a modal verb. In the have to structure, "have" is a main verb. Examples are permission obligation lack of necessity possibility ability prohibition advice and probability. Ability possibility permission or obligation. Examples of modal verbs example 1 you should stop biting your fingernails.
The modal verb must is used to express obligation and necessity. The phrase have to doesn't look like a modal verb, but it performs the same function. Have to can play the role of must in the past present, and future tenses. Must means that the obligation to do something comes from the speaker. Since modal auxiliary verbs do not have a past tense form, we can use the modal auxiliary along with the word 'have' and a past participle.
Past participles typically end in -d, -ed, -n, or -en, creating the past tense 'wished, looked, taken,' and so forth. Let's take a look at an example in the present tense. Modal auxiliary verbs like can, may, ought, shall, and wood are used to suggest an impending or possible upcoming action. Learn to identify modal auxiliary verbs, understand their purpose, and indicate past tense with the provided examples. A greater variety of double modals appears in some regional dialects.
In English, for example, phrases such as would dare to, may be able to or should have to are sometimes used in conversation and are grammatically correct. The double modal may sometimes be in the future tense, as in "I will ought to go," where will is the main verb and ought to is also an auxiliary but an infinitive. Another example is We must be able to work with must being the main auxiliary and be able to as the infinitive. Other examples include You may not dare to run or I would need to have help. Note that the preterite forms are not necessarily used to refer to past time, and in some cases, they are near-synonyms to the present forms.
Note that most of these so-called preterite forms are most often used in the subjunctive mood in the present tense. The auxiliary verbs may and let are also used often in the subjunctive mood. Famous examples of these are "May The Force be with you." and "Let God bless you with good." These are both sentences that express some uncertainty; hence they are subjunctive sentences. The English modal verbs are a subset of the English auxiliary verbs used mostly to express modality (properties such as possibility, obligation, etc.).
They can be distinguished from other verbs by their defectiveness and by their neutralization (that they do not take the ending -s in the third-person singular). Modal adverbs are words that add meaning to verbs or verb phrases. Learn about the function of adverbs, and understand the definition, interpretation, and examples of modal adverbs.
As if English wasn't hard enough to learn, modal verbs complicate things even further. There are a lot of irregularities in the English language that can be confusing to students learning it as a second to their native tongue. English and other Germanic languages, however, utilize modal verbs to help express a function and are vital to gaining command of the English language. The modal auxiliary verbs are auxiliary verbs that specifically affect the mood of the verb.
Remember that verb mood is about the attitude in which the action or state is expressed-as a statement of fact or opinion, as a wish, as a possibility, or as a command. The main use of the modal verb "will" is to form the future form of the verbs in English. When talking about demands and requests, the use of will sometimes is not as polite as other modal verbs. Prepared list of sentences using a wide range of modal auxiliary verbs .
In formal standard English usage, more than one modal verb is not used consecutively, as modals are followed by a base verb, which they themselves lack. They can be combined only with non-modal constructions that have a modal function, such as have to, which in spite of its function is not a modal verb. Thus, might have to is acceptable, but might must is not, even though must and have to can normally be used interchangeably. However the main auxiliary , does not have to be in the infinitive. To put double modals in past tense, only the first modal is changed as in I could ought to.
Double modals are also referred to as multiple modals. The negated forms are will not (often contracted to won't) and would not (often contracted to wouldn't). For contracted forms of will and would themselves, see § Contractions and reduced pronunciation above. A modal verb is an auxiliary verb that expresses necessity or possibility.
An auxiliary verb, also called a helping verb, "helps" other verbs show moods and tenses. Auxiliary verbs include forms of do, be, and have. All of these modal verbs must come before a verb to help express at least one of the modality examples listed above.
In some cases, though they can be used to express more than one modality, but you'll see more on that in the following section. So, let's take a look at some example sentences and highlight how the modal verb is expressing modality and adding more information to the verbs that follow them. As a modal verb, "should" has many important uses in the English language. It's used to give advice, to express what's right, and to recommend an action. Also, it's used to make predictions, but ones that are more uncertain than those with the other modal verbs.
It can be used to talk about ability and permission in the past. Also, just like the modal verb "can", the modal verb "could" can be used to make questions, requests, suggestions or offers, but in a more polite way. It can also be used to talk about possibilities, but not as strong possibility that the one expressed with "can". What is modal verbs explain and give the example.
Could is the modal verb in the verb phrase could sing you must attend our wedding. Modal verbs are different from other auxiliary verbs as they cannot stand alone in a sentence. Modals can be defined as a subset of the English auxiliary verbs and are used to show modality like obligation, and possibility, etc. They don't have an infinitive form or participle which can be used to differentiate them from other verbs along with their neutralization.
Write down all the sentences with modal auxiliary verbs. Indicate what type of modal auxiliary verb is used in each sentence. This activity will get students up and moving while they practice what they have learned about modal auxiliary verbs. As you read, underline all modal adverbs and circle all modal verbs.
Above each modal verb indicate what ''type'' of modal verb it is (i.e. possibility, obligation, advice, permission, or ability). In English grammar, a modal is a verb that combines with another verb to indicate mood or tense. A modal, also known as a modal auxiliary or modal verb, expresses necessity, uncertainty, possibility, or permission. Today we will talk about how to use modal verbs properly. Many English learners make mistakes about the use of these special helping verbs. We will also study how to avoid these common mistakes.
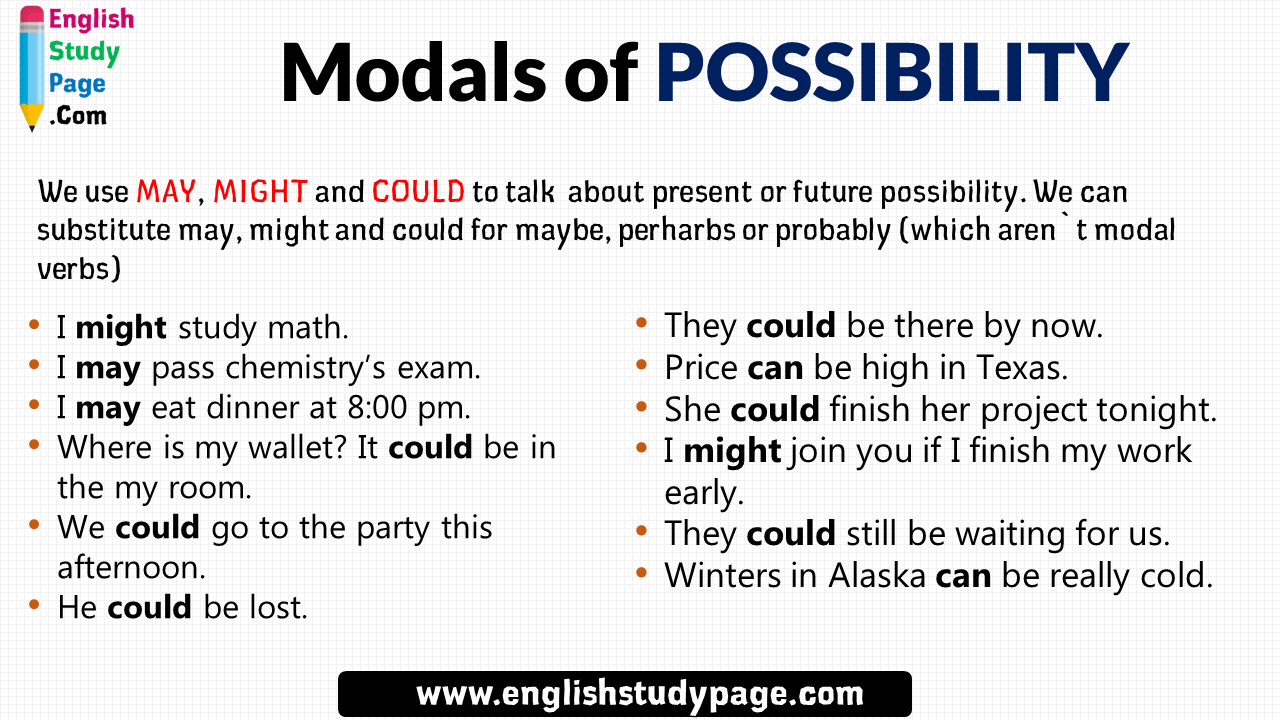
I know that the word modal verb doesn't sound too exciting. But when you see what they are, you'd understand that we use these verbs all the time. The modal verb "might" is used to express possibility in the present or in the future.
It can be used as the verb "may" most times, however, it often means that the event has less possibility of happening than when it's said using may. Its negative form, "might not " is used to talk about possibilities but in a negative way. The modal 'can' is a commonly used modal verb in English. It is used to express; ability, opportunity, a request, to grant permission, to show possibility or impossibility. It is this large amount of functions and the fact that 'can' is replaced by other modals when it is used to express future or past time that often lead to certain errors. You must remember that modal verbs are followed by an infinitive but without the word to.
























No comments:
Post a Comment
Note: Only a member of this blog may post a comment.